The COVID-19 pandemic, officially known as the coronavirus disease 2019, has reshaped the global landscape in ways that will be remembered for decades to come. This highly contagious respiratory illness, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has not only posed a significant health threat but also triggered a myriad of socioeconomic and political changes unparalleled in modern history. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the COVID-19 pandemic, its origins, transmission dynamics, global response efforts, and the far-reaching consequences it has had on society, economics, and the future of public health.
The Origin of SARS-CoV-2
The initial cases of COVID-19 were reported in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, and soon thereafter, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared it a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on January 30, 2020. The virus, SARS-CoV-2, is closely related to other coronaviruses that caused severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2002-2003 and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) since 2012. While the exact origins of SARS-CoV-2 remain under investigation, early studies suggest it likely originated from an animal-to-human transmission, possibly from bats via an intermediate host.
Transmission Dynamics and Pandemic Spread
COVID-19 is primarily spread through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. These droplets can land in the mouths or noses of nearby individuals, leading to infection. Additionally, the virus can survive on surfaces for hours to days, allowing for indirect transmission through touch. The combination of high infectivity rates and the absence of effective treatment or vaccine at the outset of the pandemic facilitated its rapid global spread. By March 2020, COVID-19 had become a full-blown pandemic, with cases reported in over 150 countries.
Global Response Efforts
In response to the unprecedented crisis, governments, international organizations, and private sectors worldwide implemented a range of measures to contain the virus's spread and mitigate its impact. These include:
Lockdowns and Social Distancing: Governments imposed lockdowns and encouraged social distancing to reduce the number of contacts between individuals, thereby slowing down the virus's transmission.
Travel Restrictions: Border closures and travel bans aimed to prevent international spread and buy time for domestic containment efforts.
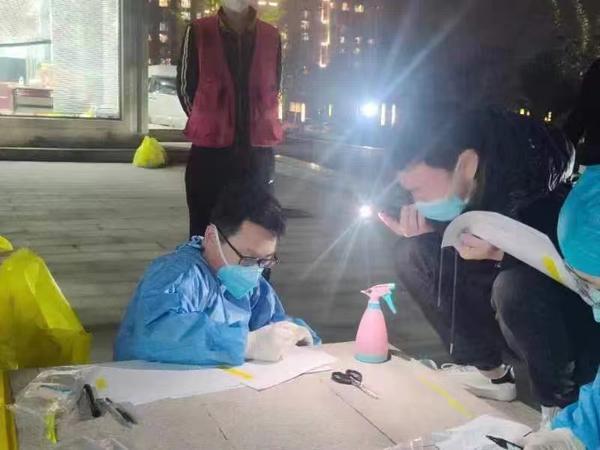
Testing and Tracing: Mass testing campaigns and contact tracing applications were launched to identify and isolate infected individuals quickly, thereby breaking transmission chains.
Vaccine Development: An unprecedented global effort saw the rapid development and deployment of COVID-19 vaccines, with several vaccines achieving emergency use authorization by late 2020.
Economic Stimulus Packages: Governments introduced massive fiscal stimulus packages to cushion the economic impact of lockdowns on businesses and individuals, including direct cash transfers, tax reliefs, and loan guarantees.
Impact on Health Systems and Lives
The pandemic has overwhelmed health systems in many countries, particularly those with weak infrastructure. Hospitals have been overwhelmed with patients requiring intensive care, while healthcare workers have been at the forefront of the fight against the virus, facing a high risk of infection themselves. The pandemic has also highlighted disparities in access to healthcare, with low-income countries struggling to provide even basic medical care to their populations.
The psychological toll of the pandemic cannot be underestimated. People have experienced anxiety, depression, and loss of income and loved ones. The fear of contracting the virus has led to social isolation and loneliness, exacerbating mental health issues globally.
Economic Consequences
The pandemic has had a devastating impact on global economies. Businesses have been forced to close or operate at reduced capacity, leading to job losses on a massive scale. The International Labour Organization estimates that over 6% of the global workforce became unemployed due to the pandemic. The service sector, which includes hospitality, tourism, and retail, has been particularly hard hit. Additionally, supply chain disruptions have led to shortages of essential goods and services worldwide.
Political and Social Ramifications
The pandemic has also brought about significant political and social changes. It has exposed weaknesses in global governance and cooperation, leading to debates about the distribution of vaccines and financial aid among nations. The pandemic has fueled mistrust in institutions and governments, particularly in cases where misinformation or slow responses were perceived. There have been protests against lockdown measures and calls for greater transparency and accountability from leaders.
The pandemic has also accelerated trends towards digitalization and remote work, reshaping how we interact socially and professionally. While this has brought convenience and efficiency, it has also widened the digital divide, exacerbating inequalities between those with access to technology and those without.
Lessons Learned and Future Prospects
The COVID-19 pandemic serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of our global society and the need for collective action in times of crisis. Key lessons include the importance of investing in public health infrastructure, strengthening global cooperation in health emergencies, promoting scientific research and innovation for future pandemics, and addressing underlying social and economic inequalities that can exacerbate health risks.
Looking ahead, as vaccination rates increase and life gradually returns to some form of normalcy, it is crucial to maintain vigilance against new variants of the virus and continue to invest in public health preparedness. The pandemic has also underscored the need for resilient economic models that can withstand shocks like pandemics while promoting social inclusion and equity.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic is a defining moment in modern history, one that has reshaped our understanding of public health emergencies, economic systems, and societal dynamics. As we navigate this new reality, it is essential to learn from our experiences, strengthen our global response mechanisms, and work towards a more resilient and equitable future that is better prepared to face future health crises. The journey ahead will be challenging, but with collective effort and a renewed commitment to science and humanity, we can emerge stronger from this trying time.
转载请注明来自爬爬百科,本文标题:《COVID-19疫情,全球社会的全面概述及其影响》











 京ICP备11000001号
京ICP备11000001号
发表评论