Introduction
The year 2020 marked a turning point in global health history with the emergence of a novel coronavirus, later named SARS-CoV-2, which caused a severe respiratory illness known as Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). This unprecedented pandemic has reshaped our daily lives, disrupted economic activities worldwide, and tested the resilience of healthcare systems across nations. This article provides an overview of the COVID-19 pandemic, its origins, transmission dynamics, global impact, and the efforts undertaken to combat it.
Origins and Early Outbreak
The first cases of COVID-19 were reported in December 2019 in Wuhan, the capital city of China's Hubei province. The virus was traced to a seafood market that sold live animals, suggesting an initial animal-to-human transmission. However, subsequent investigations revealed that the virus had likely originated from an unknown source within the city's Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market or had spread from an earlier, undetected human-to-human transmission. On January 30, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC), marking the start of a global health crisis.
Transmission Dynamics and Characteristics
SARS-CoV-2 is an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the family Coronaviridae. It is primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. These droplets can land in the mouths or noses of nearby individuals, leading to infection. Additionally, the virus can survive on surfaces for hours to days, allowing indirect contact transmission through touching contaminated objects and then touching one's face.
COVID-19 is highly contagious, with a basic reproduction number (R0) estimated to be between 2.5 and 3.5, meaning one infected person can transmit the virus to 2.5 to 3.5 others on average. Symptoms range from mild to severe and can include fever, cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, loss of taste or smell, among others. While some individuals experience only mild symptoms or are asymptomatic, others develop severe illness requiring hospitalization and potentially leading to death. The elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions are more vulnerable to severe outcomes.
Global Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had far-reaching consequences on multiple fronts:
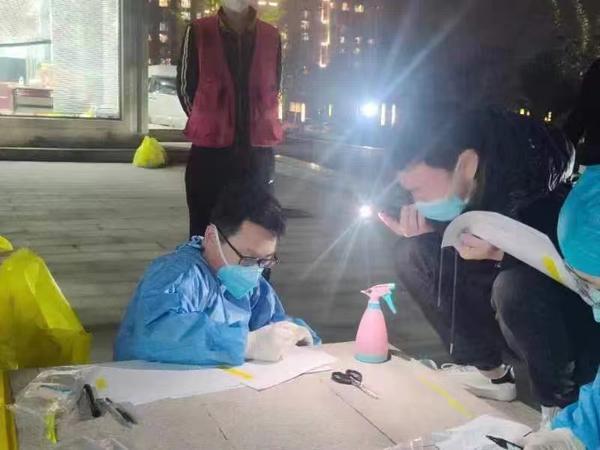
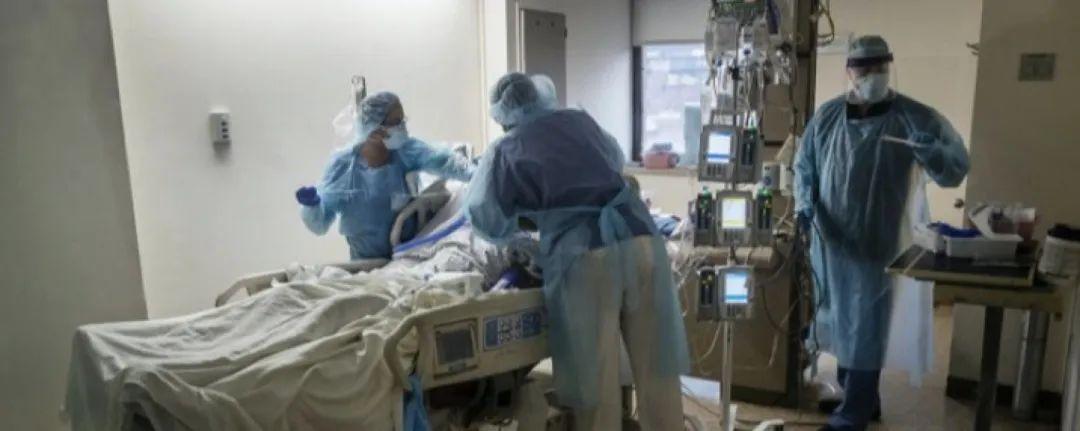
1、Health Systems: Healthcare systems in numerous countries have been overwhelmed due to the sheer volume of cases, necessitating the reallocation of resources and personnel. Intensive care units have been particularly stressed, with many countries reporting shortages of ventilators and other life-saving equipment.
2、Economic Disruption: The pandemic has triggered a global economic recession, with businesses closing their doors, supply chains disrupted, and unemployment rates skyrocketing. The tourism, hospitality, and aviation industries have been particularly hard hit. Governments worldwide have implemented economic stimulus packages and fiscal measures to mitigate the economic fallout.
3、Social Distancing and Lockdowns: To slow the spread of the virus, governments have imposed various levels of social distancing measures and lockdowns. These measures have significantly altered daily life routines, including school closures, work from home policies, and restrictions on public gatherings. The psychological impact on individuals and communities has been profound, with increased rates of anxiety, depression, and domestic violence reported.
4、Vaccine Development and Distribution: In a race against time, scientists around the world worked tirelessly to develop vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. In 2020 and 2021, several vaccines were approved for emergency use, offering hope for a potential end to the pandemic. However, vaccine inequality remains a significant challenge, with many countries struggling to access these life-saving tools due to logistical barriers and financial constraints.
5、Travel Restrictions and Border Closures: International travel came to a standstill as countries implemented travel bans and closed their borders to non-essential travelers. This has not only disrupted personal lives but also hindered global cooperation in research efforts and slowed the exchange of essential goods and services.
Efforts to Combat the Pandemic
In response to the pandemic, several international and national efforts have been undertaken:
Scientific Research: Researchers from various disciplines have collaborated to understand the virus's behavior, develop diagnostic tools, and explore treatment options. This includes studies on viral genetics, drug repurposing for potential therapies, and vaccine development.
Vaccine Distribution: The COVAX facility was established as a global initiative to ensure equitable access to COVID-19 vaccines for all countries. It aims to pool resources and coordinate with manufacturers to ensure that even low-income countries can receive vaccines.
Public Health Measures: Governments have promoted public health measures such as wearing masks, social distancing, hand hygiene, and regular testing to mitigate the spread of the virus. These measures have been shown to be effective in reducing transmission rates but require sustained adherence from the population.
Digital Solutions: The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital technologies in healthcare delivery, education, and communication. Telemedicine has become a crucial tool for maintaining access to healthcare services during lockdowns, while online learning platforms have bridged the gap for students unable to attend physical classes.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the interconnectedness of our global community and the importance of collective action in addressing public health emergencies. While we have made significant progress in developing vaccines and implementing control measures, the pandemic is far from over. The threat of new variants and vaccine resistance underscores the need for ongoing research and vigilance. As we navigate this uncertain time, it is crucial to prioritize scientific collaboration, equitable access to resources
转载请注明来自爬爬百科,本文标题:《COVID-19疫情,新型冠状病毒爆发概览》











 京ICP备11000001号
京ICP备11000001号
发表评论