The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has reshaped the world as we know it. Since its first reported case in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, the virus has spread rapidly across borders, infecting millions and causing a significant global health and economic crisis. This article provides an overview of the COVID-19 pandemic, including its origins, transmission dynamics, global impact, response measures implemented by governments and international organizations, and the ongoing efforts towards vaccination and recovery.
Origins and Early Outbreak
The initial cases of COVID-19 were linked to the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan, a large market known for selling live animals and seafood. The virus was initially thought to have originated from animals but later confirmed to be transmitted between humans. The first cases were identified in December 2019, but the true extent of the outbreak was not fully understood until January 2020 when the World Health Organization (WHO) was alerted.
Transmission Dynamics
COVID-19 is primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or exhales. These droplets can land in the mouths or noses of nearby people, leading to infection. Additionally, the virus can survive on surfaces for hours or days, making indirect contact transmission possible. The virus is highly contagious and can spread easily in closed or poorly ventilated spaces with poor hygiene practices.
Global Spread and Impact
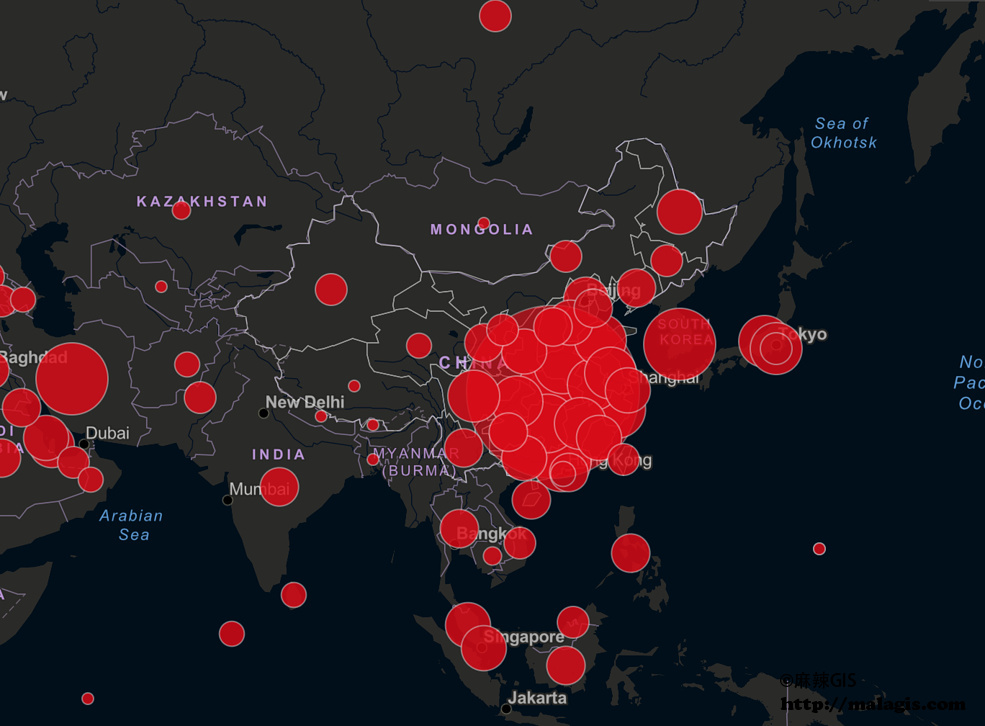
The rapid spread of COVID-19 across international borders was facilitated by global travel and trade networks. By March 2020, the pandemic had been declared a global health emergency by the WHO, marking a turning point in the global response to the crisis. As of this writing, more than 600 million confirmed cases have been reported worldwide, with over 6.5 million deaths attributed to COVID-19. The pandemic has had far-reaching consequences on public health, economies, education, and daily life.
Public Health Impact
The pandemic has led to a surge in hospitalizations and deaths worldwide. The elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions are particularly vulnerable to severe illness and death. The virus has also shown signs of mutating over time, though most variants have not significantly impacted vaccine effectiveness. However, some variants, such as the Delta and Omicron strains, have been associated with increased transmissibility and potential for evading immune responses.
Economic Impact
The pandemic has had a devastating impact on global economies. Businesses have been forced to close or operate with reduced capacity, leading to job losses and economic stagnation. The tourism, hospitality, and aviation industries have been particularly hard hit, with many facing bankruptcy or significant financial losses. Governments have implemented various measures such as lockdowns, travel bans, and subsidies to mitigate the economic fallout but have also incurred significant debt in the process.
Social Impact
The pandemic has disrupted daily life on a massive scale. Schools have been closed for extended periods, disrupting education for millions of children worldwide. Social distancing measures have led to a decline in social interactions and community cohesion. Mental health issues have surged as people grapple with fear of infection, loss of loved ones, and economic uncertainty. The pandemic has also highlighted inequalities in access to healthcare and essential services, further widening existing social divides.
Response Measures
Governmental Responses
Governments around the world have implemented a range of measures to contain the spread of COVID-19. These include:
Lockdowns and Social Distancing: Governments have imposed lockdowns or curfews to limit movement and encourage social distancing. This has been accompanied by restrictions on public gatherings, closure of non-essential businesses, and school closures.
Travel Bans and Quarantine Measures: Many countries have imposed travel bans or required quarantine for travelers arriving from high-risk areas to prevent the spread of the virus.
Testing and Tracing: Widespread testing campaigns have been launched to identify cases early and implement contact tracing to isolate and monitor close contacts. This has been crucial in containing outbreaks in some countries but has also raised concerns about privacy and surveillance.
Vaccination Programs: Vaccination programs have been rolled out globally as one of the most effective ways to control the pandemic. Governments have worked with pharmaceutical companies to procure vaccines and implement vaccination campaigns targeting priority groups such as healthcare workers and the elderly.
International Cooperation and Support
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of international cooperation and solidarity. The WHO has played a central role in coordinating the global response, providing technical guidance, sharing information on best practices, and advocating for equitable access to vaccines and resources. The United Nations (UN) agencies and other international organizations have also mobilized resources to support member states in their efforts to combat the pandemic.
Scientific Research and Vaccine Development
Scientists around the world have worked tirelessly to understand COVID-19 and develop effective treatments and vaccines. The rapid development of vaccines using mRNA technology was a significant breakthrough in the fight against the pandemic. Several vaccines were developed within a record timeframe and have been shown to be safe and effective at preventing severe illness and death from COVID-19. However, vaccine nationalism and unequal distribution remain significant challenges that require global cooperation to address.
转载请注明来自爬爬百科,本文标题:《COVID-19大流行,全面概述》











 京ICP备11000001号
京ICP备11000001号
发表评论