The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has reshaped the world as we know it since its first reported case in December 2019 in Wuhan, China. This highly contagious respiratory illness has spread rapidly across borders, infecting millions and causing a significant global health and economic crisis.
Origin and Spread:
COVID-19 is believed to have originated from Wuhan, China, where an initial cluster of cases was identified in late 2019. The virus quickly spread to other parts of China and then globally, with the World Health Organization (WHO) declaring it a pandemic on March 11, 2020. The primary mode of transmission is through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks, making social distancing and mask-wearing crucial in preventing its spread.
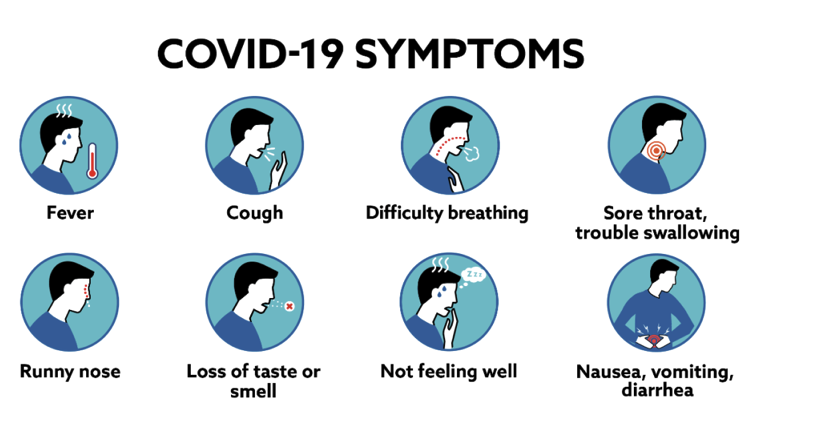
Symptoms:
While some individuals experience mild symptoms or none at all, others develop severe illness requiring hospitalization. Common symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, and loss of taste or smell. In severe cases, COVID-19 can lead to pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and even death.
Impact on Health Systems:
The pandemic has overwhelmed health systems worldwide, leading to a shortage of medical supplies such as ventilators, personal protective equipment (PPE), and vaccines. It has also strained hospital resources, with many healthcare workers contracting the virus while caring for patients. The pandemic has disproportionately affected older adults and those with pre-existing health conditions.
Economic Impact:
The economic fallout from the pandemic has been profound. Governments implemented lockdown measures to slow the spread of the virus, resulting in business closures, job losses, and a decline in global trade and tourism. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) estimates that the pandemic could cause a global recession unlike any seen since the Great Depression.
Vaccination Efforts:
In response to the crisis, scientists around the world raced to develop vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. Several vaccines were successfully tested and rolled out in late 2020 and early 2021, offering a glimmer of hope for ending the pandemic. Vaccine distribution has been uneven, with some countries receiving more doses than others due to logistical challenges and global vaccine hoarding. Nevertheless, widespread vaccination efforts have helped to reduce the severity of outbreaks and ease restrictions in many countries.
Public Health Measures:
To combat the spread of COVID-19, governments have implemented various public health measures including mandatory mask-wearing in public spaces, social distancing guidelines, and widespread testing and tracing programs. Countries have also encouraged digital solutions like online education and work-from-home policies to minimize face-to-face interactions.
Future Outlook:
While the pandemic continues to evolve, with new variants emerging periodically, the global community remains hopeful that we can eventually return to some form of normalcy. Continued research on treatments and vaccines, along with adherence to public health measures, are crucial for managing the virus's impact. Additionally, efforts to strengthen healthcare systems and promote global cooperation are vital for future pandemics.
In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic has been a defining moment in modern history, testing our resilience as a society and highlighting the importance of collaboration and scientific progress in addressing global health crises. As we navigate this unprecedented time, it is essential to remain informed, practice preventive measures, and support one another in our collective efforts to overcome this challenge.
转载请注明来自爬爬百科,本文标题:《全球疫情,COVID-19大流行病的简述》











 京ICP备11000001号
京ICP备11000001号
还没有评论,来说两句吧...