Introduction
The year 2020 marked a turning point in the history of global health, as the world was plunged into an unprecedented crisis—the COVID-19 pandemic. This highly contagious respiratory illness, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, swiftly spread across borders, disrupting economies, education systems, and daily life worldwide. This handwritten report aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the COVID-19 pandemic, its impact on society, and the measures taken globally to combat it.
Origin and Spread of COVID-19
The first cases of COVID-19 were reported in December 2019 in Wuhan, China. Initially, the virus was met with limited attention, but as cases rapidly escalated, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared it a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on January 30, 2020. By March 2020, the pandemic was declared a global pandemic, marking the start of a worldwide health crisis.
The virus's rapid spread was fueled by international travel and trade, as well as inadequate initial testing and reporting in the early stages. The first wave of infections primarily affected Asia, but soon spread to Europe, North America, and other continents. The virus's high R0 (basic reproduction number)—the average number of people an infected person will pass the virus to—made it highly contagious and difficult to contain.
Impact on Health Systems
The COVID-19 pandemic has overwhelmed healthcare systems in many countries, leading to a surge in hospital admissions and deaths. The virus has disproportionately affected older adults and those with pre-existing health conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory illnesses. In some countries, healthcare workers have been at the forefront of the fight against the pandemic, putting themselves at high risk of infection due to a lack of adequate personal protective equipment (PPE) and the sheer volume of patients.
The pandemic has also exposed gaps in global health preparedness and response mechanisms. Countries with weak health infrastructure have been particularly vulnerable, leading to a disproportionate burden on their populations. The WHO has emphasized the importance of strengthening health systems globally to better prepare for future pandemics.
Economic Impact
The economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has been profound and far-reaching. Governments worldwide have implemented lockdown measures, travel restrictions, and business closures to slow the spread of the virus. These measures have led to a sharp decline in economic activity, resulting in job losses, reduced production, and a decline in global trade. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) estimates that the pandemic could cause a global recession on par with or worse than the 2008 financial crisis.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have been particularly hard hit due to their limited financial resilience and inability to adapt quickly to changing market conditions. The loss of income for millions has led to increased poverty and food insecurity, further exacerbating pre-existing social inequalities.
Education Disruptions
Schools and universities were among the first institutions to close during the pandemic, leading to a sudden shift to online learning for millions of students worldwide. While this measure helped slow the spread of the virus, it also exposed significant digital divides, with many students lacking access to reliable internet or devices necessary for remote learning. The disruption of education has had long-term consequences for children's mental health, social development, and future prospects.
The pandemic has also highlighted the importance of education as a basic human right and underscored the need for equitable access to quality education for all. Many countries have since implemented strategies to bridge the learning gap caused by the pandemic, including providing laptops and internet access to students in need and offering flexible learning options for all students.
Social and Psychological Effects
The COVID-19 pandemic has had profound social and psychological effects on individuals and communities. Social distancing measures have led to feelings of isolation, loneliness, and depression among both children and adults. The loss of loved ones due to the virus has caused immense grief and trauma for many families. The pandemic has also fueled misinformation and conspiracy theories, which have further complicated efforts to combat the virus through effective communication and vaccination campaigns.
Mental health services have been overwhelmed in many countries due to the increased demand for support during this stressful time. Governments and international organizations have emphasized the importance of mental health support for both frontline workers and the general population, advocating for accessible services and resources during this challenging period.
Vaccination Efforts and Public Health Measures
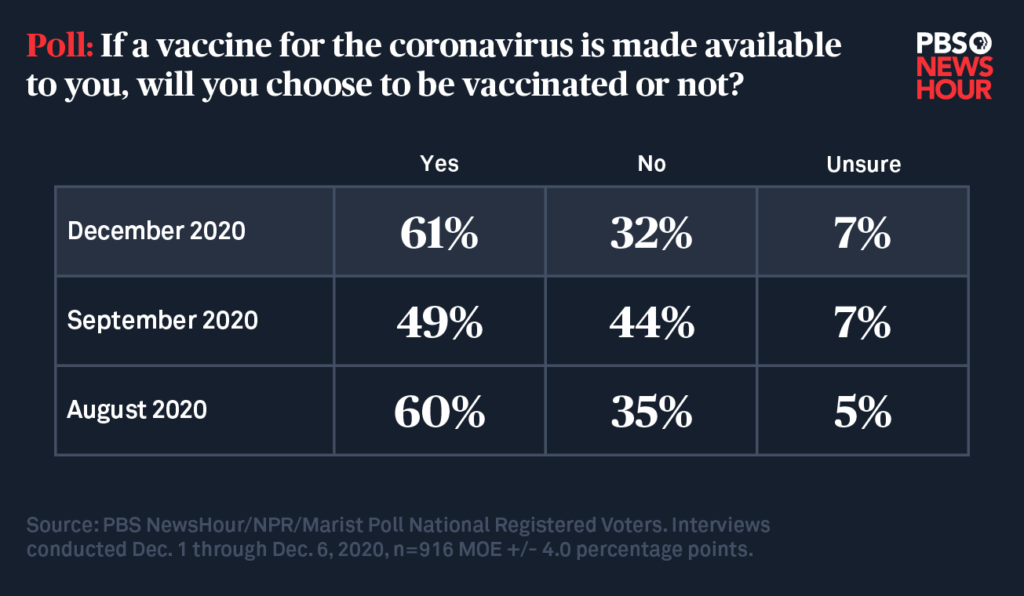
The development of vaccines against COVID-19 represented a turning point in the fight against the pandemic. Multiple vaccines were developed through unprecedented collaboration between researchers, pharmaceutical companies, and governments within a record timeframe. Vaccine distribution has been a complex process involving logistical challenges, cold chain management, and equitable access concerns. High-income countries have administered vaccines at a faster rate than low- and middle-income countries, highlighting the need for global cooperation in ensuring equitable access to vaccines worldwide.
Public health measures such as wearing masks, social distancing, hand hygiene, and avoiding crowded places remain crucial in preventing the spread of COVID-19. Governments have also implemented vaccination passports as a means of facilitating safe travel and reopening economies while ensuring that vulnerable populations are protected from new variants of the virus.
Conclusion: Building Resilience for Future Pandemics
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of global cooperation, innovation in science and technology, and investment in public health infrastructure. As we move forward from this crisis, it is essential to learn from our experiences and build resilience for future pandemics. This includes strengthening healthcare systems worldwide, investing in research and development for new vaccines and treatments, promoting digital inclusion for equitable access to education and information, and fostering global collaboration on public health issues.
The COVID-19 pandemic is a reminder that we are all connected in our vulnerability to global health threats. By working together towards common goals of public health security
转载请注明来自爬爬百科,本文标题:《COVID-19大流行,一份全面的英文手写报告》










 京ICP备11000001号
京ICP备11000001号
发表评论